Tennis elbow, or lateral epicondylitis, is a common overuse injury that can cause significant pain and functional limitations. Despite its name, it doesn’t just afflict tennis players; anyone who repeatedly uses their forearm muscles can develop this painful condition. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for prevention and management.
While tennis elbow can affect individuals of all ages and activity levels, early recognition and appropriate treatment can facilitate recovery and prevent long-term complications. By understanding tennis elbow’s causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to manage this condition and maintain their overall quality of life. If you’re experiencing symptoms of tennis elbow, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
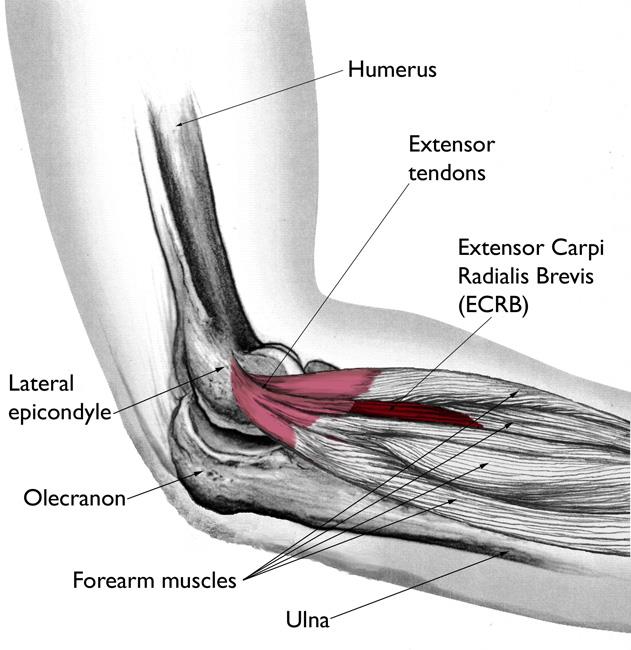
Causes of Tennis Elbow:
Tennis elbow typically develops from repetitive wrist and arm motions. While tennis players often experience this condition due to the repetitive swinging of the racket, it can also occur in individuals who engage in activities such as painting, typing, carpentry, or playing musical instruments like the violin or guitar. These activities involve repetitive gripping, twisting, or lifting motions, putting strain on the tendons around the elbow joint. The repeated stress leads to small tears in the tendons that attach to the lateral epicondyle, the bony bump on the outer part of the elbow. Over time, these tears can lead to inflammation and pain.
Dr. Sunshine discusses tennis elbow:
In the following video, Dr. Sunshine treats a patient in his office using a simple, painless injection procedure.
Symptoms of Tennis Elbow:
The hallmark symptom of tennis elbow is pain and tenderness on the outer part of the elbow. This pain may radiate down the forearm and worsen with specific movements, such as gripping, lifting, or twisting the wrist. Extending the wrist, like shaking hands or turning a doorknob, can also aggravate the symptoms.
In some cases, individuals may experience weak grip strength, making it challenging to perform daily tasks or participate in sports and recreational activities.
Diagnosis of Tennis Elbow:
Diagnosing tennis elbow typically involves a physical examination and discussing the patient’s medical history and activities. Your healthcare provider may perform specific tests to assess the range of motion in your elbow and the strength of your forearm muscles. In some cases, imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI scans may be ordered to rule out other conditions or to evaluate the extent of tissue damage.
Other Treatments of Tennis Elbow:
Treatment for tennis elbow may involve a combination of conservative measures to reduce pain and inflammation and promote healing. Here are some standard treatment options:
- Rest and Modification of Activities: Resting the affected arm and avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms is essential for allowing the tendons to heal. Modifications in technique or equipment may be recommended for athletes or individuals whose work involves repetitive motions.
- Ice Therapy: Applying ice packs to the affected area can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. Ice therapy is typically applied for 15-20 minutes several times daily, especially after activities that worsen symptoms.
- Physical Therapy: A structured physical therapy program can help strengthen the muscles around the elbow, improve flexibility, and promote healing. Therapeutic exercises, stretching techniques, and ultrasound or electrical stimulation modalities may be utilized.
- Bracing or Splinting: Wearing a brace or splint can support the elbow and reduce strain on the tendons during activities. These devices are often worn during sports or repetitive tasks to prevent further injury.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or naproxen may be recommended to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be administered directly into the affected area to provide short-term relief from pain and inflammation.
- Surgery: In severe cases where conservative treatments fail to provide relief, surgery may be recommended to repair the damaged tendons. Surgical options include tendon release or removal of damaged tissue.
Prevention of Tennis Elbow:
Preventing tennis elbow involves avoiding repetitive motions that strain the elbow tendons. Proper technique, ergonomic equipment, and regular breaks during repetitive activities can help reduce the risk of developing this condition. Strengthening the forearm muscles through targeted exercises and maintaining overall fitness and flexibility can also help prevent injury.
We hope this information is helpful. At OC Sports and Wellness in Orange County, we understand the importance of balancing your health amidst a busy lifestyle. We offer convenient options for scheduling visits, texting, or video chatting with Dr. Sunshine. Let’s work towards your well-being! We invite you to reach out: 949-460-9111



